# Lambda 表达式
- Lambda 表达式:带有参数变量的表达式
- Lambda 表达式由参数列表、箭头(
->)和 Lambda 主体组成 - 基本语法:
(parameters) -> expression或(parameters) -> { statements; }(注意表达式与语句的区别) - Java 编译器可以从上下文(目标类型)推断出用什么函数式接口来配合 Lambda 表达式,因此可以在 Lambda 语法中省去标注参数类型,当 Lambda 仅有一个类型需要推断的参数时,参数名称两边的括号也可以省略
- 在 Lambda 主体中引用的局部变量必须使用
final修饰或事实上最终的(类似匿名内部类)
# 函数式接口
- 有且仅有一个抽象方法的接口(@FunctionalInterface 注解用于表示该接口会设计成一个函数式接口),如 Comparator<T>、Runnable、Callable<V>
# 函数描述符
- 函数式接口的抽象方法的签名(Lambda 表达式的签名)
- 特殊的 void 兼容规则:如果一个 Lambda 的主体是一个语句表达式,它就和一个返回 void的函数描述符兼容
# 使用 Lambda
- Lambda 表达式以内联的形式为函数式接口的抽象方法提供实现,并把整个表达式作为函数式接口的一个实例(即 Lambda 表达式是函数式接口一个具体实现的实例)
- 作用:传递代码片段
- 注意:只有在接受函数式接口的地方才可以使用 Lambda 表达式
# 常见的函数式接口
| 函数式接口 | 抽象方法 | 函数描述符 | 默认方法 | 静态方法 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comparator<T> | int compare(T o1, T o2) | (T,T) -> int | reversed, thenComparing | naturalOrder, comparing, comparingInt, comparingLong, comparingDouble, reverseOrder, nullsFirst, nullsLast |
| Runnable | void run() | () -> void | ||
| Callable<V> | V call() | () -> V | ||
| Predicate<T> | boolean test(T t) | T -> boolean | and, or, negate | |
| BiPredicate<T, U> | boolean test(T t, U u) | (T,U) -> boolean | ||
| Consumer<T> | void accept(T t) | T -> void | andThen | |
| BiConsumer<T, U> | void accept(T t, U u) | (T,U) -> void | ||
| Supplier<T> | T get() | () -> T | ||
| Function<T,R> | R apply(T t) | T -> R | andThen, compose | identity |
| BiFunction<T, U, R> | R apply(T t, U u) | (T,U) -> R | ||
| UnaryOperator<T> | T apply(T t) | T -> T | ||
| BinaryOperator<T> | Tt apply(T t1, T t2) | (T,T) -> T | minBy, maxBy |
// 自定义的函数式接口,把受检异常转换为运行时异常
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ThrowingFunction<T, R, E extends Throwable> {
static <T, R, E extends Throwable> Function<T, R> unchecked(ThrowingFunction<T, R, E> f) {
return t -> {
try {
return f.apply(t);
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
};
}
R apply(T t) throws E;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 方法引用
- 基本语法:
目标引用 :: 方法名 - 作用:直接传递现有的方法实现
- 方法引用主要有四类(仅有一个方法调用的 Lambda 方法体)
- 指向静态方法的方法引用,
args -> ClassName.staticMethod(args)等价ClassName::staticMethod - 指向任意类型的实例方法的方法引用,
(arg0, rest) -> arg0.instanceMethod(rest)等价ClassName::instanceMethod(arg0 的类型是 ClassName) - 指向现有对象的实例方法的方法引用,
args -> expr.instanceMethos(args)等价expr::instanceMethod - 构造函数引用,
ClassName::new(需要有无参构造器)
- 指向静态方法的方法引用,
# 流
- java.util.stream.Stream
- 流:从支持数据处理操作的源生成的元素序列
- 集合是一个内存中的数据结构,包含数据结构中目前所有的值,其主要目的是以特定的时间/空间复杂度存储和访问元素
- 流是在概念上固定的数据结构,其元素是按需计算的(即延迟计算),流的目的在于表达计算
注意:流只能操作一次,否则会抛出异常:java.lang.IllegalStateException: stream has already been operated upon or closed
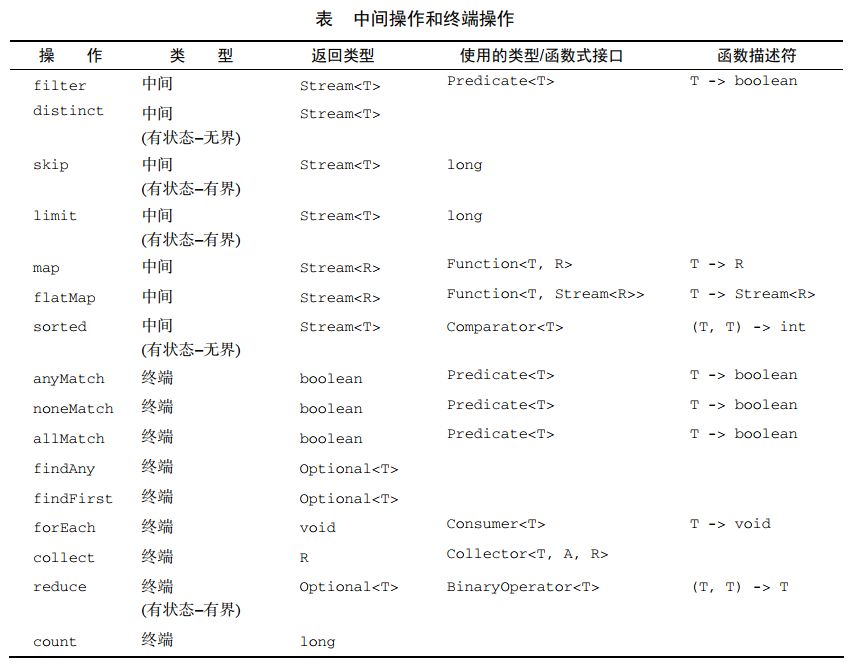
# 流操作
可分为两类操作
- 中间操作(intermediate operation):可以连接起来的流操作,中间操作会返回另一个流
- 终端操作(terminal operation):关闭流的操作,终端操作会从流的流水线生成结果(任何不是流的值)
除非流水线上触发一个终端操作,否则中间操作不会执行任何处理(延迟执行)
流的使用一般包括三件事:
- 一个数据源(如集合)来执行一个查询
- 一个中间操作链,形成一条流的流水线
- 一个终端操作,执行流水线,并能生成结果
# 使用流
# 筛选
Stream<T> filter(Predicate<T> predicate):用谓词筛选,返回一个包括所有符合谓词的元素的流(用谓词筛选)Stream<T> distinct():返回一个元素各异(根据流所生成元素的 hashCode 和 equals 方法实现)的流(筛选各不相同的元素)// distinct elements by property or key static <T> Predicate<T> distinctByKey(Function<? super T, ?> keyExtractor) { Map<Object, Boolean> seen = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); return t -> seen.putIfAbsent(keyExtractor.apply(t), Boolean.TRUE) == null; } list.stream().filter(distinctByKey(b -> b.getName()));1
2
3
4
5
6
# 切片
Stream<T> limit(long maxSize):返回一个不超过给定长度的流(截短流)Stream<T> skip(long n):返回一个扔掉了前 n 个元素的流(跳过元素)
# 映射
提取或转换流中的元素
Stream<R> map(Function<T, R> mapper):对流中每一个元素应用函数(元素映射为新元素)Stream<R> flatMap(Function<T, Stream<R>> mapper):把一个流中的每个元素都换成另一个流,然后把所有转换的流连接起来成为一个流(流的扁平化)(元素映射为流)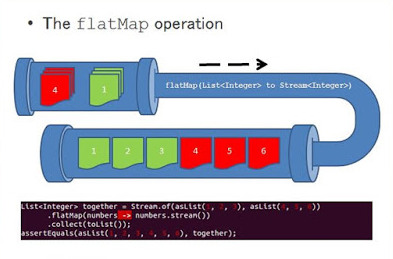
# 查找和匹配
boolean allMatch(Predicate<T> predicate):流中的元素是否都能匹配给定的谓词boolean anyMatch(Predicate<T> predicate):流中是否有一个元素能匹配给定的谓词boolean noneMatch(Predicate<T> predicate):流中是否没有任何元素与给定的谓词匹配Optional<T> findAny():返回当前流中的任意元素Optional<T> findFirst():返回当前流中的第一个元素
# 归约
- 将流中所有的元素迭代合并成一个结果
Optional<T> reduce(BinaryOperator<T> accumulator)T reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> accumulator):初始值 identity,accumulator 将两个流元素结合起来并产生一个新值(适用于不可变的归约)U reduce(U identity, BiFunction<U, T, U> accumulator, BinaryOperator<U> combiner):Optional<T> min(Comparator<T> comparator):根据提供的 Comparator 返回此流的最小元素Optional<T> max(Comparator<T> comparator):根据提供的 Comparator 返回此流的最大元素R collect(Collector<T, A, R> collector)R collect(Supplier<R> supplier, BiConsumer<R, T> accumulator, BiConsumer<R, R> combiner):自定义收集器的供应源 supplier、累加器 accumulator、组合器 combiner
# Collector 接口
// T - 流中元素的类型,A - 累加器的类型,R - 收集操作的结果对象的类型
public interface Collector<T, A, R> {
Supplier<A> supplier(); // 建立新的结果容器
BiConsumer<A, T> accumulator(); // 将元素添加到结果容器(累加器是原位更新)
BinaryOperator<A> combiner(); // 合并两个结果容器
Function<A, R> finisher(); // 对结果容器应用最终转换
Set<Collector.Characteristics> characteristics(); // 定义收集器的行为:UNORDERED、CONCURRENT、IDENTITY_FINISH
// UNORDERED——归约结果不受流中元素的遍历和累积顺序的影响
// CONCURRENT——accumulator 函数可以从多个线程同时调用,且该收集器可以并行归约流(如果收集器没有标为 UNORDERED,则仅在用于无序数据源时才可以并行归约)
// IDENTITY_FINISH——完成器方法返回的函数是一个恒等函数,可以跳过,即累加器对象 A 将会直接用作归约过程的最终结果 R
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 自定义收集
// 将 Stream<T> 中的所有元素收集到一个 List<T>
// 方法 1:自定义 Collector
public class ToListCollector<T> implements Collector<T, List<T>, List<T>> {
@Override
public Supplier<List<T>> supplier() {
return ArrayList::new; // 创建集合操作的起始点
}
@Override
public BiConsumer<List<T>, T> accumulator() {
return List::add; // 累积遍历过的项目,原位修改累加器
}
@Override
public BinaryOperator<List<T>> combiner() {
return (list1, list2) -> {
list1.addAll(list2); // 修改第一个累加器,将其与第二个累加器的内容合并
return list1; // 返回修改后的第一个累加器
};
}
@Override
public Function<List<T>, List<T>> finisher() {
return Function.identity(); // 恒等函数
}
@Override
public Set<Characteristics> characteristics() {
// 为收集器添加 IDENTITY_FINISH和 CONCURRENT标志
return Collections.unmodifiableSet(EnumSet.of(IDENTITY_FINISH, CONCURRENT));
}
}
List<Dish> dishes = menuStream.collect(new ToListCollector<Dish>());
// 方法 2:对于 CONCURRENT 和 IDENTITY_FINISH 但并非 UNORDERED 的收集操作
List<Dish> dishes = menuStream.collect(ArrayList::new, List::add, List::addAll);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
// 查找 Stream<T> 中出现次数最多的元素 T
public class MostFrequentCollector<T> implements Collector<T, Map<T, Integer>, Optional<T>> {
@Override
public Supplier<Map<T, Integer>> supplier() {
return HashMap::new;
}
@Override
public BiConsumer<Map<T, Integer>, T> accumulator() {
return (acc, elem) -> acc.merge(elem, 1, Integer::sum);
}
@Override
public BinaryOperator<Map<T, Integer>> combiner() {
return (a, b) -> Stream.concat(a.entrySet().stream(), b.entrySet().stream())
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Map.Entry::getKey, summingInt(Map.Entry::getValue)));
}
@Override
public Function<Map<T, Integer>, Optional<T>> finisher() {
return (acc) -> acc.entrySet().stream()
.reduce(BinaryOperator.maxBy(Map.Entry.comparingByValue()))
.map(Map.Entry::getKey);
}
@Override
public Set<Characteristics> characteristics() {
return Collections.emptySet();
}
}
Stream.of(1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5).collect(new MostFrequentCollector<>()).get(); // 2
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
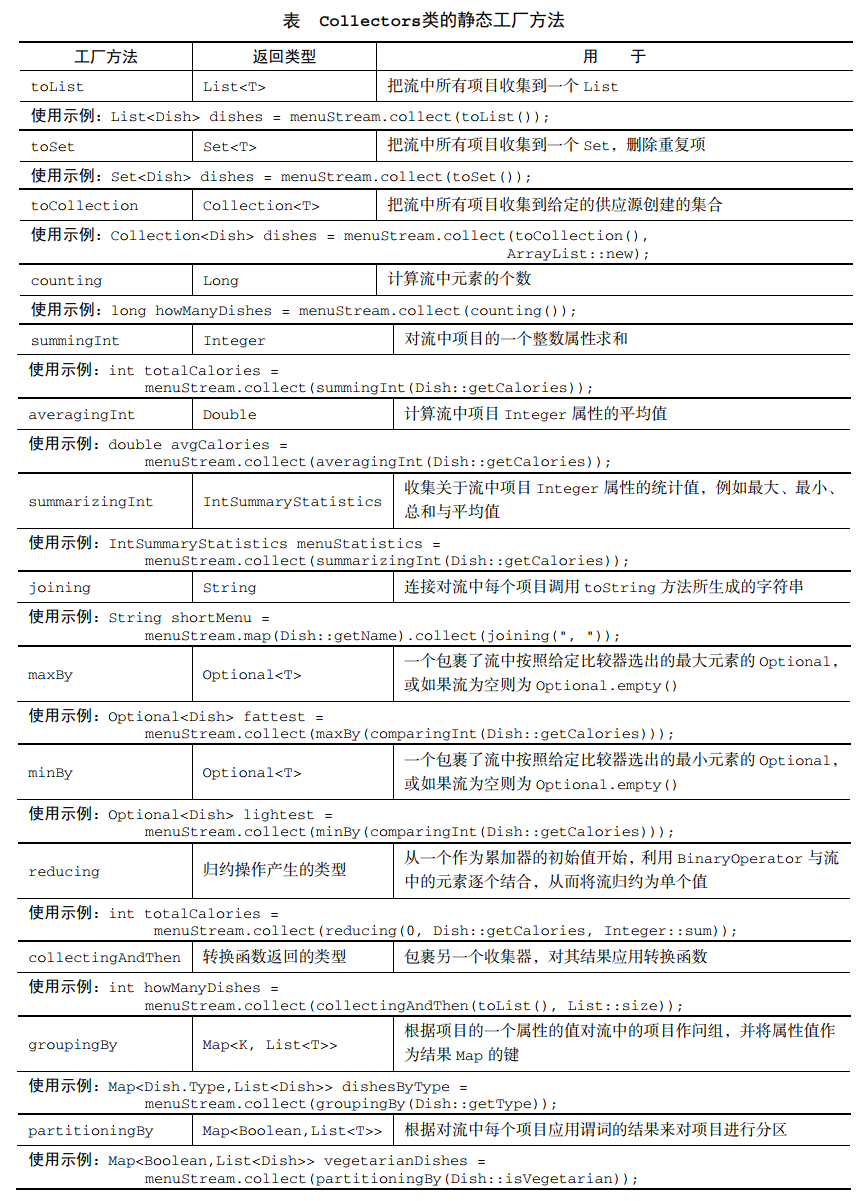
# 预定义收集器
- Collectors 实用类中提供了很多静态工厂方法用于创建常见的收集器 collector 的实例,这些收集器主要提供三大功能
将流元素归约和汇总为一个值
- 计算流中元素的个数:Collectors.counting
- 最大值和最小值:Collectors.maxBy、Collectors.minBy,返回类型是 Optional<T>
- 汇总:求和 Collectors.summingInt、Collectors.summingLong、Collectors.summingDouble;求平均数 Collectors.averagingInt、Collectors.averagingLong、Collectors.averagingDouble
- 收集关于流中元素 Integer 属性的统计值(元素个数、总和、平均值、最大值、最小值等):Collectors.summarizing
- 连接对流中每个元素调用 toString 方法所生成的字符串:Collectors.joining
- 广义的归约汇总:
Collector<T, ?, Optional<T>> reducing(BinaryOperator<T> op)
Collector<T, ?, T> reducing(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> op)
Collector<T, ?, U> reducing(U identity, Function<T, U> mapper, BinaryOperator<U> op):归约操作的起始值 identity(也是流中没有元素时的返回值),转换函数 mapper,累积函数 op 将两个转换得到的结果累积成一个同类型的值(使用于可变的归约)
元素分组
Collector<T, ?, Map<K, List<T>>> groupingBy(Function<T, K> classifier):分组函数 classifier 把流中的元素分成不同的组,把分组函数返回的值作为映射的键,把流中所有具有这个分类值的元素的列表作为对应的映射值,groupingBy(f)实际上是groupingBy(f, HashMap::new, Collectors.toList())的简便写法(注意:分组函数的返回值即映射的键不能为 null)Collector<T, ?, Map<K, D>> groupingBy(Function<T, K> classifier, Supplier<M> mapFactory, Collector<T, A, D> downstream):下游的收集器 downstream 对分到同一组中的所有流元素执行进一步归约操作,可实现多级分组、按子组收集数据等
Map<String, Map<String, Summary>> sumMap = stuList.stream() .collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getClassName, Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getGender, Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), stus -> { int score1Total = 0, score2Total = 0; for (Student student : stus) { score1Total += student.getScore1(); score2Total += student.getScore2(); } // int score1Total = stus.stream().mapToInt(Student::getScore1).sum(); // int score2Total = stus.stream().mapToInt(Student::getScore2).sum(); Student stu = stus.get(0); return new Summary(stu.getClassName(), stu.getGender(), score1Total, score2Total); })) ));1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15元素分区
Collector<T, ?, Map<Boolean, List<T>>> partitioningBy(Predicate<T> predicate):分区函数 predicate,得到的分组 Map 的键类型是 Boolean,最多可以分为两组Collector<T, ?, Map<Boolean, D>> partitioningBy(Predicate<T> predicate, Collector<T, A, D> downstream)
其它
Collector<T, ?, List<T>> toList():把流中所有元素收集到一个 ArrayListCollector<T, ?, Set<T>> toSet():把流中所有元素收集到一个 HashSet,删除重复项Collector<T, ?, Map<K, U>> toMap(Function<T, K> keyMapper, Function<T, U> valueMapper):收集到一个 HashMapCollector<T, ?, Map<K, U>> toMap(Function<T, K> keyMapper, Function<T, U> valueMapper, BinaryOperator<U> mergeFunction):Collectors.toMap(Pair::getKey, Pair::getValue, (v1, v2) -> v2), HashMap::new);Collector<T, ?, M> toMap(Function<T, K> keyMapper, Function<T, U> valueMapper, BinaryOperator<U> mergeFunction, Supplier<M> mapSupplier):keyMapper - 产生 key 的映射函数;valueMapper - 产生 value 的映射函数(产生的 value 不能为 null);mergeFunction - 一个合并函数,用于解决与相同 key 相关联的 value 之间的冲突,提供给Map.merge(Object, Object, BiFunction);mapSupplier - 返回一个新的空的 Map 的函数,其中将插入结果Collector<T, ?, C> toCollection(Supplier<C> collectionFactory):把流中所有项目收集到给定的供应源创建的集合Collector<T, A, RR> collectingAndThen(Collector<T, A, R> downstream, Function<R, RR> finisher):包裹另一个收集器,对其结果应用转换函数 finisher 把收集器的结果转换为另一种类型Collector<T, ?, R> mapping(Function<T, U> mapper, Collector<U, A, R> downstream):mapper 对流中的元素做变换,downstream 将变换的结果对象收集起来
# 其它
long count():返回此流中的元素数void forEach(Consumer<T> action):对此流的每个元素执行操作void forEachOrdered(Consumer<T> action):按流中元素的顺序对此流的每个元素执行操作Stream<T> sorted():返回由此流的元素组成的流,根据自然顺序排序(要求流中元素的类型必须实现 Comparable 接口)Stream<T> sorted(Comparator<T> comparator):返回由此流的元素组成的流,根据提供的 Comparator 进行排序S unordered():把有序流变成无序流,S 是 BaseStream 的实现类型Stream<T> peek(Consumer<T> action):返回由该流的元素组成的流,另外在从生成的流中消耗元素时对每个元素执行提供的操作(拆分)Object[] toArray():返回一个包含此流的元素的数组A[] toArray(IntFunction<A[]> generator):使用 generator 函数返回的数组收集此流的元素,函数的输入
# 静态方法
Stream<T> concat(Stream<T> a, Stream<T> b):合并两个流
# 数值流
- 流有三种基本的原始类型特化:IntStream、DoubleStream 和 LongStream,流中的元素类型分别为 int、long 和 double
- 原始类型流映射到数值流
IntStream mapToInt(ToIntFunction<T> mapper)LongStream mapToLong(ToLongFunction<T> mapper)DoubleStream mapToDouble(ToDoubleFunction<T> mapper)
数值流转换回对象流
Stream<Integer> boxed()、Stream<Long> boxed()、Stream<Double> boxed():装箱Stream<U> mapToObj(IntFunction<U> mapper)、Stream<U> mapToObj(LongFunction<U> mapper)、Stream<U> mapToObj(DoubleFunction<U> mapper)
数值流之间的相互转换
IntStream mapToInt(LongToIntFunction mapper)、IntStream mapToInt(DoubleToIntFunction mapper)LongStream mapToLong(IntToLongFunction mapper)、LongStream mapToLong(DoubleToLongFunction mapper)DoubleStream mapToDouble(IntToDoubleFunction mapper)、DoubleStream mapToDouble(LongToDoubleFunction mapper)
# 类方法
IntStream range(int startInclusive, int endExclusive)、LongStream range(long startInclusive, long endExclusive):生成某个范围内的数字,不包含结束值IntStream rangeClosed(int startInclusive, int endInclusive)、LongStream rangeClosed(long startInclusive, long endInclusive):生成某个范围内的数字,包含结束值
# 实例方法
OptionalInt max()、OptionalLong max()、OptionalDouble max():求最大值OptionalInt min()、OptionalLong min()、OptionalDouble min():求最大值int sum()、long sum()、double sum():求和,默认返回 0IntSummaryStatistics summaryStatistics()
# 构建流
从集合创建
- 使用 Collection 接口中的抽象方法
Stream<E> stream()创建一个流
- 使用 Collection 接口中的抽象方法
由值创建流
- 使用 Stream 类中静态方法
Stream.of(T... values)通过显式值创建一个流 - 使用 Stream 类中静态方法
Stream.empty(),创建一个空流
- 使用 Stream 类中静态方法
由数组创建流
- 使用 Arrays 类中静态方法
Arrays.stream(T[] array)从数组创建一个流
- 使用 Arrays 类中静态方法
由文件生成流
- 使用 Files 类中静态方法
Files.lines(Path path, Charset cs),返回一个由指定文件中的各行构成的字符串流
- 使用 Files 类中静态方法
由函数生成流:创建无限流,然后使用 limit 限制流元素个数
- 迭代:使用 Stream 类中静态方法
Stream.iterate(T seed, UnaryOperator<T> f),依次对每个新生成的值应用函数 f,流的第一个元素是初始值 seed - 生成:使用 Stream 类中静态方法
Stream.generate(Supplier<T> s):流的每个元素由 s 提供
- 迭代:使用 Stream 类中静态方法
# 并行流
parallelStream()parallel():把顺序流转成并行流sequential():把并行流转成顺序流并行流背后使用的基础架构是 Java 7 中引入的 Fork/Join 分支/合并框架(以递归方式将可以并行的任务拆分成更小的任务,在不同的线程上执行,然后将每个子任务的结果合并起来生成整体结果)
默认使用公共的线程池 ForkJoinPool,即
ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),默认并行度是 CPU 核数 - 1,因此只适用于处理 CPU 密集型任务// 设置公共 ForkJoinPool 的并行度 System.setProperty("java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.common.parallelism", "7"); private static final boolean useCommonPool = (ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism() > 1); // Default executor -- ForkJoinPool.commonPool() unless it cannot support parallelism. // ThreadPerTaskExecutor 每来一个任务就起一个线程执行 private static final Executor asyncPool = useCommonPool ? ForkJoinPool.commonPool() : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor();1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# CompletableFuture<T>
- implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T>
- 组合式异步编程
# 静态方法
CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier):使用公共的线程池 ForkJoinPool 执行异步任务CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor):使用指定的线程池执行异步任务- 组合多个 CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs):等待数组中的所有 CompletableFuture 对象都执行完毕,返回一个 CompletableFutureCompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs):只要数组有任何一个 CompletableFuture 对象执行完毕就不再等待,返回由第一个执行完毕的 CompletableFuture 对象的返回值构成的 CompletableFuture
# 实例方法
T join():阻塞直到返回完成时的结果值,如果遇到异常则抛出 unchecked exception- 定义处理 CompletableFuture 的返回结果,即回调函数
CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action)CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action)CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T, ? extends U> fn)
- 组合两个 CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn):对两个异步操作进行流水线,第一个操作完成后,将其结果作为参数传递给第二个操作CompletableFuture<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn):当两个 CompletableFuture 对象完成计算后,将结果合并
- 异常处理(如果异常发生,
res参数将是 null,否则ex将是 null)ConnectionFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable, ? extends T> fn):仅在异常时回调,可在异常时返回特定值用于回退ConnectionFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action):无论异常是否发生都会被调用ConnectionFuture<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn):无论异常是否发生都会被调用,可在异常时返回特定值用于回退
xxxAsync 重载方法默认使用公共的线程池 ForkJoinPool 执行操作,可通过设置 executor 参数指定使用的线程池
// 用户信息查询
final UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
CompletableFuture userFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
getRemoteUserAndFill(id, userInfo);
return Boolean.TRUE;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture bonusFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
getRemoteBonusAndFill(id, userInfo);
return Boolean.TRUE;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture growthFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
getRemoteGrowthAndFill(id, userInfo);
return Boolean.TRUE;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture.allOf(userFuture, bonusFuture, growthFuture).join();
userFuture.get();
bonusFuture.get();
growthFuture.get();
// userInfo
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
// 由于流操作之间的延迟特性,需要使用不同的 Stream 流水线
// 即先收集所有 CompletableFuture 对象,再在新的流中获取结果
// 让 Future 在完成操作之前就能启动其它 Future
// 查询美元和欧元之间的转换汇率
CompletableFuture<BigDecimal> exchangeRateFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> exchangeService.getRate(Money.EUR, Money.USD), executor);
List<CompletableFuture<String>> priceFutures = shops.stream()
// 查询指定商店中特定商品的价格
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> shop.getPrice(product), executor)
// 组合两个 CompletableFuture,将价格和汇率做乘法计算出汇后价格
.thenCombine(exchangeRateFuture, (price, rate) -> price * rate)
.thenApply(price -> shop.getName() + " price is " + price)
.exceptionally((e) -> {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
return "Unknown!";
}))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// List<String> prices = priceFutures.stream()
// .map(CompletableFuture::join)
// .collect(Collectors.toList());
// Create a combined Future using allOf()
CompletableFuture<Void> allFutures = CompletableFuture.allOf(priceFutures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[0]));
// When all the Futures are completed, call `future.join()` to get their results and collect the results in a list
CompletableFuture<List<String>> allPriceFuture = allFutures.thenApplyAsync(v -> priceFutures.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.collect(Collectors.toList()), executor);
List<String> prices = allPriceFuture.join();
// CompletableFuture.allOf(priceFutures).join(); // 等待所有 CompletableFuture 对象执行完毕
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
// 如果父子任务都从同一个线程池中获取线程,并且父任务需要等待子任务执行完成,在并发情况下,可能会因为子任务进了队列,导致父任务一直等待,最终导致线程池资源耗尽,出现假死现象。因此应避免父子任务共用同一个线程池。
// 如果 CompletableFuture 的默认线程池,可以正常执行完成
// 错误示例
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(100));
List<Integer> tasks = IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 5).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList());
CompletableFuture[] taskFutures = tasks.stream()
.map(task -> CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",---【任务" + task + "】开始执行---");
List<String> datas = Lists.newArrayList("a", "b");
CompletableFuture[] dataFutures = datas.stream()
.map(data -> CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",【任务" + task + "】开始处理数据=" + data);
}, threadPoolExecutor))
.toArray(CompletableFuture[]::new);
// 等待所有子任务完成
CompletableFuture.allOf(dataFutures).join(); // java.lang.Thread.State: WAITING
}, threadPoolExecutor))
.toArray(CompletableFuture[]::new);
// 等待所有父任务完成
CompletableFuture.allOf(taskFutures).join();
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# 并行计算比较
对集合进行并行计算有两种方式:
- 将其转化为并行流 parallelStream,利用 map 操作开展工作
- 循环遍历集合中的每一个元素,创建新的线程,在 CompletableFuture 内对其进行操作
如果进行的是计算密集型的操作,并且没有 I/O,推荐使用 Stream 接口
如果并行的工作单元还涉及等待 I/O 的操作(包括网络连接等待),推荐使用 CompletableFuture,并依据等待时间与计算时间的比率设定需要使用的线程数
# Optional<T>
- Optional<T> 类(java.util.Optional)是一个容器类,代表一个值存在或不存在
- 基本类型的 Optional 对象:OptionalInt、OptionalLong、OptionalDouble
# 静态方法
Optional<T> empty():返回一个空的 Optional 实例Optional<T> of(T value):返回具有指定非空值的 Optional 实例,如果该值为 null,则抛出一个 NullPointerException 异常Optional<T> ofNullable(T value):返回一个指定值的 Optional,如果值为 null,则返回一个空的 Optional
# 实例方法
boolean isPresent():在值存在时就返回 true,否则返回 falsevoid ifPresent(Consumer<T> block):在值存在的时候执行给定的代码块,否则什么也不做Optional<U> map(Function<T, U> mapper):如果值存在,就对该值执行提供的 mapping 函数调用,否则返回一个空的 Optional 对象Optional<U> flatMap(Function<T, Optional<U>> mapper):如果值存在,就对该值执行提供的 mapping 函数调用,返回一个 Optional 类型的值,否则就返回一个空的 Optional 对象(将两层的 Optional 对象转换为单一 Optional 对象)Optional<T> filter(Predicate<T> predicate):如果值存在并且满足提供的谓词,就返回包含该值的 Optional 对象;否则返回一个空的 Optional 对象T get():有值则返回值,否则抛出一个 NoSuchElementException 异常T orElse(T other):有值则返回值,否则返回 otherT orElseGet(Supplier<T> other):有值则返回值,否则调用 other 并返回该调用的结果T orElseThrow(Supplier<X> exceptionSupplier):有值则返回值,否则抛出由 exceptionSupplier 创建的异常
# 新的日期和时间 API
java.time 包中,日期-时间对象是不可变的
Temporal 的实现类:
- Instant(代表一个具体的时刻,与时区无关,相当于旧的 Date 类)
- LocalDate(代表不带时区的日期)
- LocalTime(代表不带时区的时间)
- LocalDateTime(代表不带时区的日期、时间)
- Year(代表年)
- YearMonth(代表年月)
- ZonedDateTime(代表带相对于指定时区的日期、时间,类似于 Calendar)
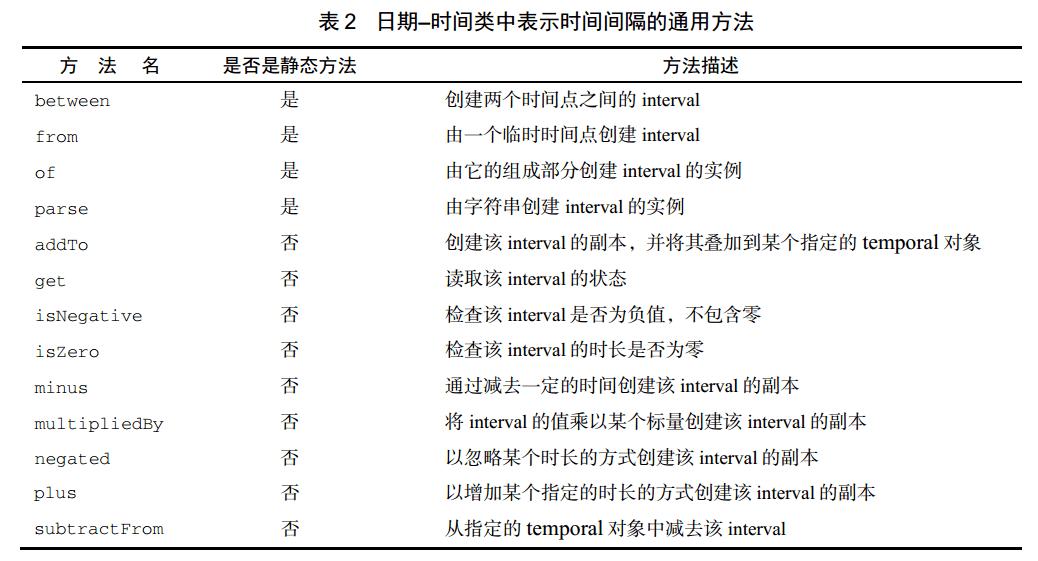
TemporalAmount 的实现类:Duration(代表以秒和纳秒衡量的时长,格式
PnDTnHnMn.nS)、Period(代表以年、月、日衡量的时长,格式PnYnMnD)ZoneId(代表一个时区)、ZoneOffset(ZoneId 的子类,代表与 UTC/格林尼治时间的绝对偏差)
Clock(用于获取指定时区的当前日期、时间)
DayOfWeek(星期枚举类)、Month(月份枚举类)
ChronoUnit(时间单位枚举类):YEARS、MONTHS、WEEKS、DAYS、HOURS、MINUTES、SECONDS、NANOS 等
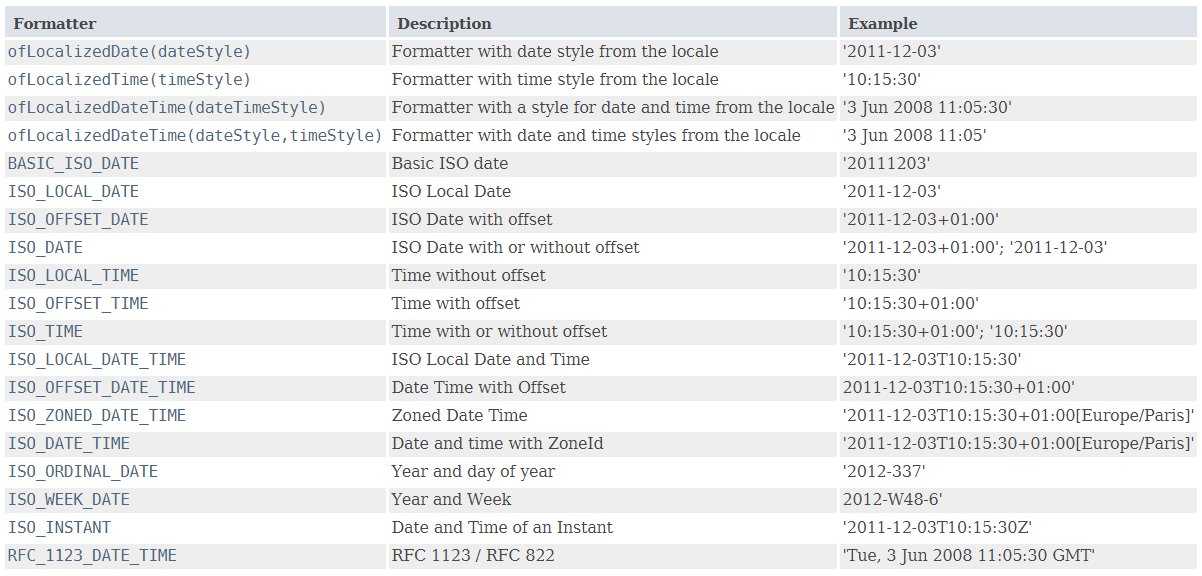
格式器类:DateTimeFormatter,其所有实例都是线程安全的
根据模式字符串来创建 DateTimeFormatter 格式器,类方法:
DateTimeFormatter ofPattern(String pattern)使用 DateTimeFormatter 格式化为字符串
- 调用 DateTimeFormatter 对象的
format(TemporalAccessor temporal)将日期、时间(LocalDate、LocalDateTime、LocalTime 等实例)格式化为字符串 - 调用 LocalDate、LocalDateTime、LocalTime 等日期、时间对象的
format(DateTimeFormatter formatter)方法执行格式化
- 调用 DateTimeFormatter 对象的
使用 DateTimeFormatter 解析字符串
通过日期、时间对象提供的parse(CharSequence text)或parse(CharSequence text, DateTimeFormatter formatter)方法解析日期、时间字符串(默认的格式是 DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME、DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE、DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_TIME,如 "2011-12-03T10:15:30.1234","T" 不区分大小写,秒和纳秒可选)
// 获取当前日期
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
today.lengthOfMonth(); // today.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH);
// 判断是否时闰年
today.isLeapYear();
// 获取当前时间
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
// 设置时间
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2018, 10, 1, 23, 59, 59);
// 获取年、月、日、时、分、秒
dateTime.getYear(); // dateTime.get(ChronoField.YEAR);
dateTime.getMonth().getValue(); // dateTime.get(ChronoField.MONTH_OF_YEAR);
dateTime.getDayOfMonth(); // dateTime.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH);
dateTime.getHour();
dateTime.getMinute();
dateTime.getSecond();
// 调整日期/时间,返回修改了属性的新对象
dateTime.withDayOfMonth(25); // dateTime.with(ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH, 25)
// 当月的最后一天
dateTime.with(TemporalAdjusters.lastDayOfMonth());
// 比较先后
dateTime.isAfter(now);
dateTime.isBefore(now);
// 加减时间
dateTime.plusDays(1); // dateTime.plus(1, ChronoUnit.DAYS);
dateTime.minusDays(1);
// 格式化
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
// LocalDateTime 转 String
formatter.format(dateTime); // dateTime.format(formatter);
// String 转 LocalDateTime
LocalDateTime.parse("2018-10-01 23:59:59", formatter);
// LocalDateTime 转 LocalDate、LocalTime
LocalDate localDate = dateTime.toLocalDate();
LocalTime localTime = dateTime.toLocalTime();
// LocalDate、LocalTime 转 LocalDateTime
dateTime = localDate.atStartOfDay(); // 一天的开始时间
localDate.atTime(LocalTime.MIDNIGHT); // 00:00:00.000000000
localDate.atTime(LocalTime.MIN); // 00:00:00.000000000
localDate.atTime(LocalTime.NOON); // 12:00:00.000000000
localDate.atTime(LocalTime.MAX); // 23:59:59.999999999
dateTime = LocalDateTime.of(localDate, localTime);
// 获取当前时间戳
long millisecond = Instant.now().toEpochMilli(); // 转换当前时间的毫秒值
long second = Instant.now().getEpochSecond(); // 获取当前时间的秒数
Instant.ofEpochMilli(millisecond); // 毫秒值转 Instant
// Instant 转 String
// Instant 时间戳没有时区信息,直接转会报错 UnsupportedTemporalTypeException: Unsupported field: YearOfEra
formatter.format(Instant.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()));
// 将此日期转换为从 1970-01-01 开始的天数
dateTime.toEpochDay();
// 将此日期时间转换为从 1970-01-01T00:00:00Z 开始的毫秒数
dateTime.toInstant(ZoneOffset.of("+8")).toEpochMilli();
// LocalDateTime 转换为 ZonedDateTime,再转换为 Instant,再转换为 Date
Date date = Date.from(dateTime.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant());
// Date 转换为 Instant,再转换为 LocalDateTime
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.ofInstant(date.toInstant(), ZoneId.systemDefault());
// 获取相差时间间隔(不能使用 Period.between() 返回的是两个日期差几年零几月零几天)
amount = start.until(end, ChronoUnit.DAYS); // end.toEpochDay() - start.toEpochDay()
amount = ChronoUnit.DAYS.between(start, end);
// 时间长度:Duration、Period
Duration d1 = Duration.between(time1, time2);
Duration d1 = Duration.between(dateTime1, dateTime2);
Duration d2 = Duration.between(instant1, instant2);
// Obtains a Period consisting of the number of years, months, and days between two dates.
Period tenDays = Period.between(date1, date2);
Period sixMonths = Period.ofMonths(6);
Duration sixSeconds = Duration.ofSeconds(6);
dateTime.plus(sixMonths);
dateTime.plus(sixSeconds);
// 时区 ID
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.systemDefault();
// ZoneId zoneId = TimeZone.getDefault().toZoneId();
// ZoneId romeZone = ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai");
zoneId.getId(); // 时区 ID:Asia/Shanghai
zoneId.getRules(); // 时区规则:ZoneRules[currentStandardOffset=+08:00]
// ZonedDateTime 有 LocalDateTime 几乎相同的方法,不同的是它可以设置时区
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.of("UTC+8"); // ZoneId.of("+8")
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.of(2018, 10, 1, 23, 59, 59, 1234, zoneId);
// 为时间点添加时区信息
ZonedDateTime zdt1 = date.atStartOfDay(zoneId); // 时间为 00:00:00
ZonedDateTime zdt2 = dateTime.atZone(zoneId);
ZonedDateTime zdt3 = instant.atZone(zoneId);
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.of("-5");
ZonedDateTime zdt = ZonedDateTime.now(); // 2020-12-17T15:31:27.870+08:00[Asia/Shanghai]
// 获取当前时刻对应的 ZonedDateTime
ZonedDateTime zdt1 = ZonedDateTime.now(zoneId); // 2020-12-17T02:31:27.870-05:00
// 通过给 LocalDateTime 附加一个 ZoneId,变成 ZonedDateTime
ZonedDateTime zdt2 = ZonedDateTime.of(now, zoneId); // 2020-12-17T15:31:27.870-05:00
ZonedDateTime zdt2 = now.atZone(zoneId); // 2020-12-17T15:31:27.870-05:00
// 时区转换
// 1. 转换为相同时刻对应的 ZonedDateTime
ZonedDateTime zdt1 = zdt.withZoneSameInstant(zoneId);// 2020-12-17T02:31:27.870-05:00
// 2. 转换为相同日期时间对应的 ZonedDateTime
ZonedDateTime zdt2 = zdt.withZoneSameLocal(zoneId);// 2020-12-17T15:31:27.870-05:00
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116

- TemporalAdjusters 工厂类中返回 TemporalAdjuster(调整器)实例的静态方法
firstDayOfMonth():当月的第一天lastDayOfMonth():当月的最后一天firstDayOfNextMonth():下月的第一天lastInMonth(DayOfWeek dayOfWeek):下月的最后一天firstDayOfNextYear():明年的第一天firstDayOfYear():当年的第一天lastDayOfYear():今年的最后一天dayOfWeekInMonth(int ordinal, DayOfWeek dayOfWeek):同一个月中,第几个符合星期几要求的值firstInMonth(DayOfWeek dayOfWeek):同一个月中,第一个符合星期几要求的值lastInMonth(DayOfWeek dayOfWeek):同一个月中,最后一个符合星期几要求的值previous(DayOfWeek dayOfWeek):在当前日期之前第一个符合指定星期几要求的日期next(DayOfWeek dayOfWeek):在当前日期之后第一个符合指定星期几要求的日期previousOrSame(DayOfWeek dayOfWeek):在当前日期之后第一个符合指定星期几要求的日期,如果当前日期已经符合要求,直接返回该对象nextOrSame(DayOfWeek dayOfWeek):在当前日期之后第一个符合指定星期几要求的日期,如果当前日期已经符合要求,直接返回该对象
# Base64
- Base64 是一种用 64 个字符来表示任意二进制数据的方法
- Base64 编码会把 3 字节的二进制数据编码为 4 字节的文本数据,,长度比原来增加 1/3
- java.util.Base64 工具类提供的静态方法用于获取以下三种 Base64 编码方案的编解码器(Base64.Encoder、Base64.Decoder)
- Basic(RFC4648):输出被映射到一组字符
A-Za-z0-9+/,编码不添加任何行标,输出的解码仅支持A-Za-z0-9+/(Base64.getEncoder()、Base64.getDecoder()) - URL and Filename safe(RFC4648_URLSAFE):输出映射到一组字符
A-Za-z0-9-_,输出是 URL 和文件(Base64.getUrlEncoder()、Base64.getUrlDecoder()) - MIME(RFC2045):输出映射到 MIME 友好格式,即输出每行不超过 76 个字符,并且使用 '\r' 并跟随 '\n' 作为分割,编码输出最后没有行分割(
Base64.getMimeEncoder()、Base64.getMimeDecoder())
- Basic(RFC4648):输出被映射到一组字符
# 内部类
Base64.Encoder,实例方法:
Encoder withoutPadding()
String encodeToString(byte[] src):使用 Base64 编码方案将指定的字节数组编码为字符串int encode(byte[] src, byte[] dst):使用 Base64 编码方案对来自指定字节数组的所有字节进行编码,将生成的字节写入给定的输出字节数组byte[] encode(byte[] src):使用 Base64 编码方案将指定字节数组中的所有字节编码为新分配的字节数组OutputStream wrap(OutputStream os):使用 Base64 编码方案包装用于编码字节数据的输出流Base64.Decoder,实例方法
byte[] decode(String src):使用 Base64 编码方案将 Base64 编码的字符串解码为新分配的字节数组byte[] decode(byte[] src):使用 Base64 编码方案从输入字节数组中解码所有字节,将结果写入新分配的输出字节数组int decode(byte[] src, byte[] dst):使用 Base64 编码方案从输入字节数组中解码所有字节,将结果写入给定的输出字节数组InputStream wrap(InputStream is):返回一个输入流,用于解码 Base64 编码字节流
# 其它语言新特性
# 注解
# 重复注解
- 要求:将注解标记为 @Repeatable,提供一个注解的容器
# 类型注解
- 从 Java 8 开始,注解已经能应用于任何类型,包括 new 操作符、类型转换、instanceof 检查、泛型类型参数,以及 implements 和 throws 子句